Aqueous Coating: A clear, fast-drying water-based coating that is used to protect printed pieces. It provides a high-gloss or matte surface that deters dirt and fingerprints.
Bindery: The finishing department, which performs operations on the printed product after it has been printed. The bindery operations are as follows: Cutting, Folding, Stitching, Scoring, Perforation, Die Cutting and more.
Bleed: Bleed must extend past the cut-line and will be trimmed from the product during the final cutting phase. When the image is required to extend all the way to the edge, bleed is needed to preserve the finished look and the quality of the final product.
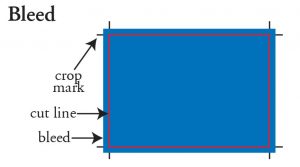
Please keep all text at least 0.125″ inside the cut-line. The bleed for most products is 0.125″ – 0.25″.
Booklets: A small group of sheets folded and generally stapled at the fold (saddle-stitched).
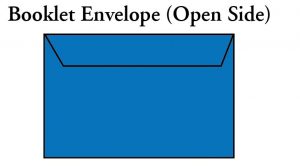
Booklet Envelope: A booklet envelope with an opening along its longest dimension.
Bulk Mail: A class of mail for sending out large numbers of identical items at a reduced rate. Also known as standard mail or third-class mail.
Business Reply Mail: This allows customers to send a reply via First-Class Mail or Priority Mail. The business pays the postage and a per piece fee only for the pieces returned. To ensure the postage is collected, clerks at the delivery Post Office calculate the amount due and withdraw the money from a customer account.

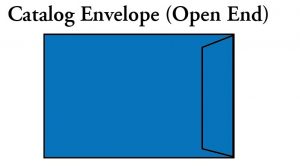
Catalog Envelope: A catalog envelope with an opening along its short dimension.
C1S paper: Manufactured paper coated one side. The term C1S (coated 1 side) refer to paper coated at the manufacturing stage, prior to printing. Coated paper has a smoother printing surface and lower ink absorption than uncoated paper.
C2S paper: Manufactured paper coated both sides. The term C2S (coated 2 sides) refer to paper coated at the manufacturing stage, prior to printing. Coated paper has a smoother printing surface and lower ink absorption than uncoated paper.
Cardstock: Also called cover stock. Mostly heavyweight papers are called cardstock. i.e. 100# gloss cover, 80# gloss cover, 14pt, 16pt.
CMYK: The primary colors used in 4-color printing. CMYK are used to reproduce full color on the printed sheet. CMYK also called PROCESS COLOR.

Coding Accuracy Support System (CASS): CASS is a certification system from the United States Postal Service (USPS) for address validation. A CASS-certified address validation service will standardize your mailing list, update outdated addresses, and verify that addresses are valid and complete.
Epson Proof: A proof showing what the final printed product will look like. Epson proofs are a 80%-85% match with the final product. Nothing will be an exact match unless it is seen on press (press proof).
Consecutive Numbering: Numbering a form, or a series of printed material where the number changes sequentially from one to another. i.e. the first one has number 100, the second will get 101, the third would be 102 and so on.
Crop Marks (Guide Marks) & Cut Line: Lines printed in the margin of sheet that indicates to the cutter and bindery where the finished product should be trimmed. They are also used to show what part of a photo should be used and what part should be cropped off.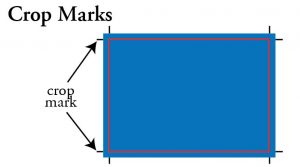
Debossing: A process of imprinting/indenting an image by applying pressure to the front side of a material to change the surface, giving it a dimensional or indented effect.
Die Cutting: A specific shape like circle, star, etc (any designs that cannot be done by a straight cut) which is cut by a metal blade. Door hangers are a popular product which requires die cutting.
Dots Per Inch (dpi): A measurement of resolution of input, output and display devices. 300 dpi means that when printed, each square inch of your image will contain 90,000 pixels (dots), the higher the dpi (the more pixels per inch) the crisper the printed image will be. Our electronic (digital files) have to have a resolution of at least 300 dpi. Anything less than that is considered as low resolution and may appear blurry when printed.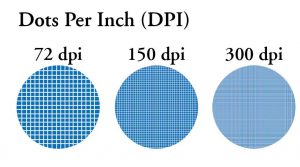
Embossing: A process of imprinting an image by applying pressure to the back side of a material to change the surface, giving it a three dimensional or raised effect.
Finished Size / Trim Size: The size of a printed product after all production operations have been completed.
Finishing: Operations to a document after it has been printed. The finishing operations could include bindery work such as, folding, trimming, binding, die cutting, inserting or any post press process that must be completed.
Flat Size: The size of a printed product after printing and trimming but before any finishing operations that affect its size, such as folding.
Foil Stamp: The application of metallic gold or silver foil on paper using a heated die. The foil is adhered to the surface leaving the design of the die on the paper. Foil stamp is generally used on invitations, presentation folders, napkins and business cards.


Folding: The process of bending printed sheets in a specific area. Folding is one of our popular bindery jobs.
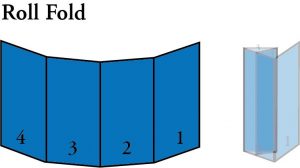
- 4-Panel Roll Fold: A type of fold where the piece is folded inward at one end and then folded inward again one or more times. It is as if you are rolling the piece up.
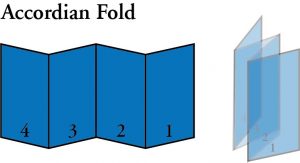
- Accordion Fold: A sheet which has been printed on only one side then folded twice in right angles to form a W-shaped four-page uncut section. Standard Accordion folds are offered as 4-panels. For 5-panel Accordion fold jobs submit a custom estimate. Accordion folds are usually available on 100lb gloss book papers. Such as, brochures and catalogs.
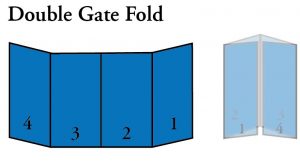
- Double Gate Fold: Single gate fold, with an additional fold on the center.
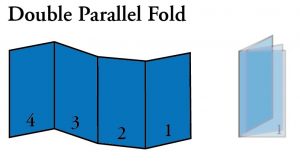
- Double Parallel Fold: A type of fold where the piece is folded in half and then folded in half again. The folds are parallel to each other.
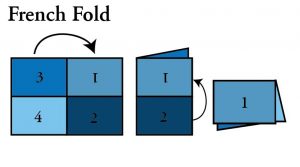
- French Fold (quarter fold): A sheet which has been printed on one side only and then folded twice at right angles to form a four-page uncut section.
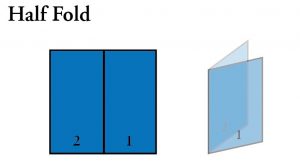
- Half Fold: A paper folded in half.
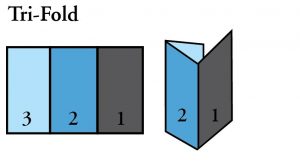
- Tri Fold: A fold where a three-panel piece has both side sections folded inward, one on top of the other each section is approximately 1/3 the length of the piece. Also known as a C-fold or letter-fold.
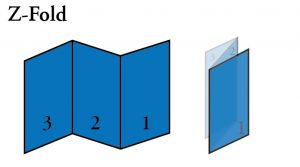
- Z Fold: A paper fold represented by back and forth folds into three panels.
Gloss Paper: Paper with a manufactured gloss finish, coated at the factory. i.e. 100# gloss book, and 100# gloss cover.
Grayscale: Grayscale refers to printing/copying in black and white (tones of gray). 
Head to Head: Printing on the front and back of a sheet is setup so that the top of both sides is printed at the same end of the sheet. You would turn the sheet like the page of a book to read the reverse side. 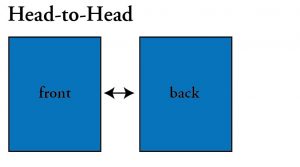
Head-to-Toe: Printing on the front and back of a sheet so that the tops of each side are printed at opposite ends from each other. The top of one side is opposite the bottom of the other. You would turn the sheet over from top to bottom to read the reverse side. Also referred to as head-to-tail or tumble. 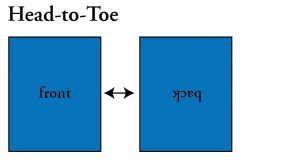
Indicia: An imprinted box in the upper right corner (see below for examples) on each mail piece that signifies the postage has been prepaid. A postal indicia takes the place of a stamp or postage meter imprint. 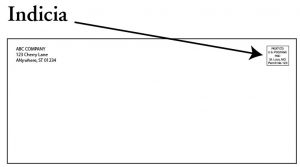
Insert: A letter, card, or similar item placed inside another mail piece (host piece).
Intelligent Mailer Barcode: A USPS-developed method to encode ZIP Code information on mail that can be read for sorting by automated machines. Intelligent Mail barcodes also encode other tracking information. All bulk mail is required to have these barcodes. ![]()
Lamination: The process of applying a film, often plastic or co-polymer, to either one or both sides of a printed sheet. Lamination adds a gloss or silk finish to a printed product and provides durability, water resistance and tear resistance.
Landscape: Printing a page so that when positioned for reading the width is greater than the height. 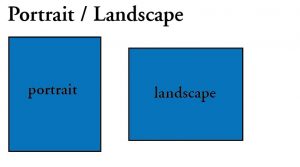
Margin: The non-printed areas around the image area of a page.
Offset Printing: The transfer of an inked image from a plate to a blanket cylinder, which in turn transfers the image to the printing material as it passes between the blanket and the impression cylinder and pressure is applied. Also referred to as offset lithography. 
Open End Envelope: A catalog envelope with an opening along its short dimension. 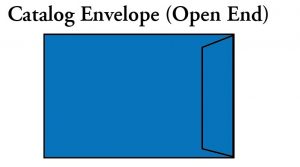
Open Side Envelope: A booklet envelope with an opening along its longest dimension. 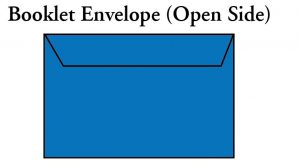
Out of Register / Off Register: When an image is not printing in the exact location that it is supposed to. When printing more than one color, if the colors do not line up properly, they are out of register.
OUT OF IN
REGISTRATION REGISTRATION

Overruns / Overs: The quantity of items produced over the quantity that was originally ordered. For digital prints, whether black & white or color, the exact quantity is run. In offset printing, there is a 10% over/under rule. The final invoice will reflect that 10% over/under charge accordingly.
Pantone Matching System (PMS): A registered name for an ink color matching system used to compare, match and identify specific colors. To do so we use a pantone book. It contains pantone colors with their closest CMYK values.

Paper Grain: The direction in which the fibers line up during the manufacturing process. It is easier to fold, bend, or tear the paper along the same direction of the fibers. Cut sheet laser printers generally use long grain paper in which the grain runs parallel to the long side of the paper, resulting in better performance through the laser printer.
Perfect Bound Books: A form of bookbinding in which the leaves are bound by gluing. It is a cost-friendly alternative to sewn hardback books. 
Perforation: Creating a series of holes so that the paper can be torn more easily along the line that is formed. Postage stamps and tear-off cards are common products that require perforation. 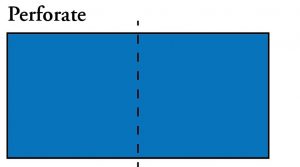
Pixel: Any of the small discrete elements that together constitute an image (as on a monitor or digital screen). More pixels per inch, the better the resolution. On computer monitors, the display is divided into rows and columns containing thousands or millions of pixels. Each pixel is composed of three dots representing the three-color channels of red, green, and blue light that are necessary for creating a color image on computer monitors and television screens. Because of their small size, the pixels appear to merge, simulating a continuous tone image, but when magnified they appear to be tiny square blocks of light, as shown in the illustration. ![]()
Plate: A metal or paper light-sensitive sheet that holds an image that has been photographically produced. During the printing process, the image area picks up ink, which is then transferred to a blanket and then to paper.
Portrait: Printing a page so that when positioned for reading the height is greater than the width. 
Presort: The process by which a mailer groups mail by ZIP Code for the USPS so that it is sorted to the finest extent required by the standards for the rate claimed.
Press Proof: A proof that is produced on the press using the inks and paper specified for that order.
Production Time (see also: The accumulated time between receipt of an order and completion of the finished product. We offer different types of turnaround depending on the product, we have Next Day, 2-4 days, 5-7 days and 7-9 business days turnaround.
Proofs: A copy of the artwork representing the finished product. It is used for review and approval. Proofs are done as a PDF emailed, hard copy or exact print of finished project.
Punching: Drilling of holes through paper. Most holes are 5/16” diameter, i.e. 3-hole punch. However other sizes are utilized for special projects such as wedding invitations for ribbons.
Quotation: A price, given by the printer or distributor, based on the specifications supplied for that product.
Register Marks: The printed marks used to align color separations for printing so that each color registers with each other. ![]()
Resolution: The measurement of output quality expressed in pixels (dots) per inch on a computer monitor or dots per inch on printed media. For example, a monitor displaying a resolution of 800 by 600 refers to a screen capable of displaying 800 pixels in each of 600 lines, which translates into a total of 480,000 pixels displayed on the screen. When referring to printed media, a 300 dpi (dots per inch) printer for example, is capable of outputting 300 dots in a one-inch line, which means that it has the ability of printing 90,000 distinct dots per square inch (300 x 300).
RGB: The additive primary colors, red, green and blue, used to display color in video monitors. Printing with a file in RGB color mode will produce a washed-out appearance. If a file is submitted in RGB, we print in CMYK and there will be a color difference. 
Roll Labels: Labels that are produced on rolls for each of machine application or manual application. Large runs of labels are most cost effective in rolls rather than sheets. 
Saddle Stitching: A method of binding folded pages that are stitched through the fold from the outside, using a wire staple (stapling).
Satin AQ: A water-based aqueous coating that helps seal and protect the printed product and provides a luxurious, satin finish.
Score: A crease applied to a sheet of paper to allow it to fold easier and more accurately. 
Shrink Wrapping: A method of wrapping packages or products with a plastic film and then applying heat so that the wrap fits tight to the product.
Slitting: A slit refers to cuts made on the pockets where business cards can then be displayed.
Silk Lamination: A dull matte film applied to one or both sides of a print product. Silk lamination give cards a luxurious smooth feel and may dull color and contrast slightly. Durable Silk lamination is tear and water resistant.
Spiral Binding: Book binding that consists of a spiral plastic that is wound through holes. Also referred to as coil binding. 
Spot UV Coating: Coating paper only in specific areas as opposed to all over coating. UV coating is applied in only specific areas and does not get any UV coating in any other places. Spot UV can be referred to as spot varnish.
Template: A preset model that acts as a structure for setting up a similar product. We have many useful templates, click here.
Turnaround Time: The accumulated time between receipt of an order and completion of the finished product. We offer different types of turnaround depending on the product, we have Next Day, 2-4 days, 5-7 days and 7-9 business days turnaround.
Typesetting: The process of converting text into type used for printing. Computers (PCs and MACs are used for this nowdays, however in the “olden days” type was put together with a series of lettered blocks. 
UPC Bar Code: A barcode is a machine-readable form of information on a visual surface that can be scanned. They are also often known as UPC codes. The barcode is read by using a special scanner that reads the information directly. The information is then transmitted into a database where it can be logged and tracked. 
UV Coating: A liquid coating applied to the printed piece, which is then bonded and cured with ultraviolet light. This coating is used to provide a protective coating to the printed image. Please note that you CAN NOT write or imprint on a UV coated jobs.
Window Envelope: An envelope with a die cut opening that is intended to have information show through from the piece inside the envelope. These come in a variety of window sizes and positions, as well as security for those documents with sensitive information. 
